What ho, wonderful people!
Nope, no pottery today. Instead we have tracks. And stones. And holes. Look, just read on… it’s simpler.
Now, I do love a good track. Ask anyone who knows me, and they’ll say “why yes, that ruggedly handsome, wonderously whiskered, and all-round splendid chap does indeed love a good track or two“. I also love a good stone. In fact, ask anyone who knows me, and they’ll say “why yes, that marvellous man, that genius gentleman, that… ” What’s that? What do you mean “get on with it!“? Honestly.
Ok, so several years ago I noticed that dotted around the Glossop area are a number of standing stones that have holes carved in them. I did wonder about them, but presumed they were a form of gatepost, even if they didn’t seem to be in a place one would expect a gatepost.

More recently I have been looking at tracks:
TRACK (noun) A rough path or road, typically one beaten by use rather than constructed.
And more specifically, the old – medieval or post-medieval (10th – 17th centuries) – trackways that dotted the area. Glossop is a great example of what we call a medieval ‘dispersed settlement’ – essentially, whilst there is a central focus – Old Glossop, with the church and market – most people actually lived in the many surrounding ‘dispersed’ farmsteads – Heath, Dinting, Ashes, Jumble, etc. People came together every Sunday for Mass, as well as other feast days and holy-days, for market days, as well as socially – for a drink in the tavern, for example. But by and large, Glossop in the medieval and early modern periods was dispersed throughout the valley in farmsteads. In this instance, a farmstead may be understood as a farmhouse and associated buildings – barns, shippons, and various ‘farm-ey’ outbuildings – as well as houses for the farmworkers. In total, we’re looking at perhaps 20 people or so for a larger farmstead, maybe 5 for a smaller. Of course, people need to travel, and roads were made through the landscape, connecting these farmsteads, and it these I incredibly interesting.

They were not just a means of physical movement through the landscape, but also a conduit for other aspects of life. As packhorse routes (no horse and carts here, just heavily laden beasts of burden) they connected everybody, and allowed goods and produce to move between places and markets. News of the wider world also moved along these tracks – a new king or a new religion, or news of battles and wonders in far off places. But so did disease and infection; the Black Death and Great Plague once walked these tracks. We also encounter the more local and personal aspects of life, too: newlyweds from church, newborns from baptisms, and the final journey from the farmstead to the church yard, as the deceased was carried for burial, often for miles, along the tracks, followed by mourning family and friends. All of life is contained in a track, worn deep by use, and all of history held there, if only we could access it.
However, the collision of stone and track didn’t connect until last year, when it occurred with an audible click at Pyegrove.

An afternoon playdate with Master Hamnett and his friend led us to Manor Park via Pyegrove. Now Pyegrove is an interesting corner of Glossop, with a long history; the name means the copse or thicket’ (grove or greve, as it is in older maps) of the magpie (the ‘Pie’ or ‘Pye’ element) which suits its location below Shire Hill perfectly. The house here has a datestone that reads “I.M.A. 1747” (no photographs, alas… it’s difficult to even see it without overtly trespassing), so that the house is at least that early. However, in the baptism record of a John Shepperd at Glossop on Christmas Day 1735, his father (Robert Shepperd the Younger) gives his address as Pyegreve, so we know something else was there at an earlier date. Pyegrove is, I suspect, another medieval farmstead… but all that (along with tales of Buffalo Bill) is for another time. Let’s return to tracks and stones.
The footpath at Pyegrove splits – right skirts Shire Hill down to Mossy Lea, left ploughs on over the playing fields to Glossop.
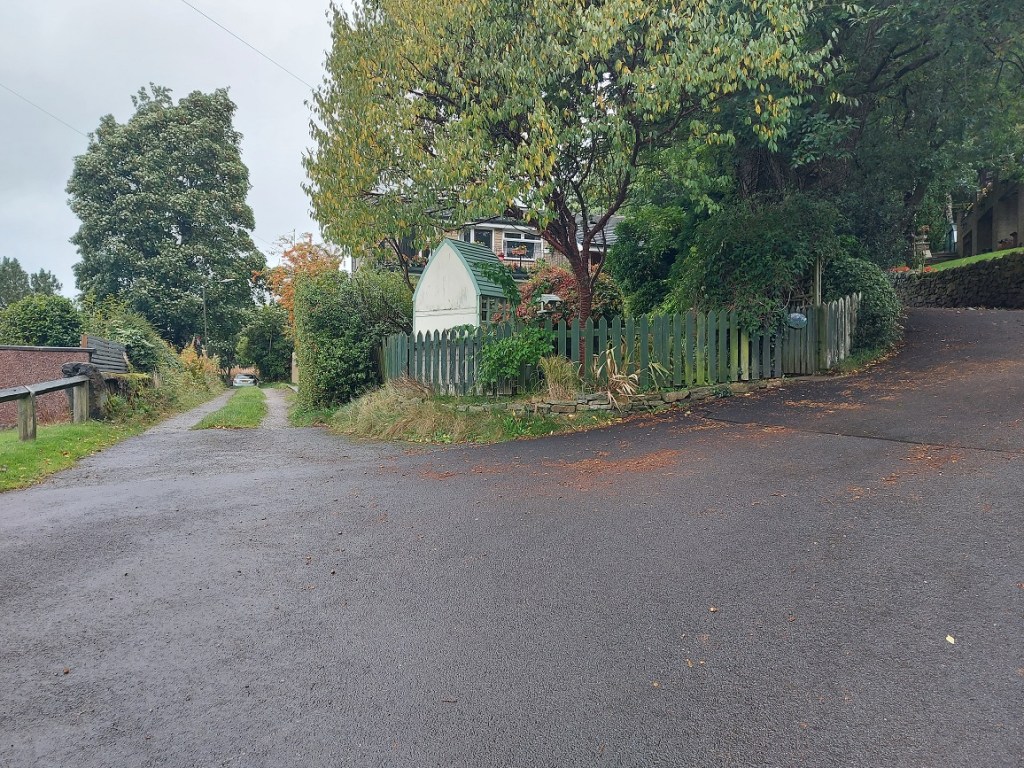

But just at the split I noticed this:
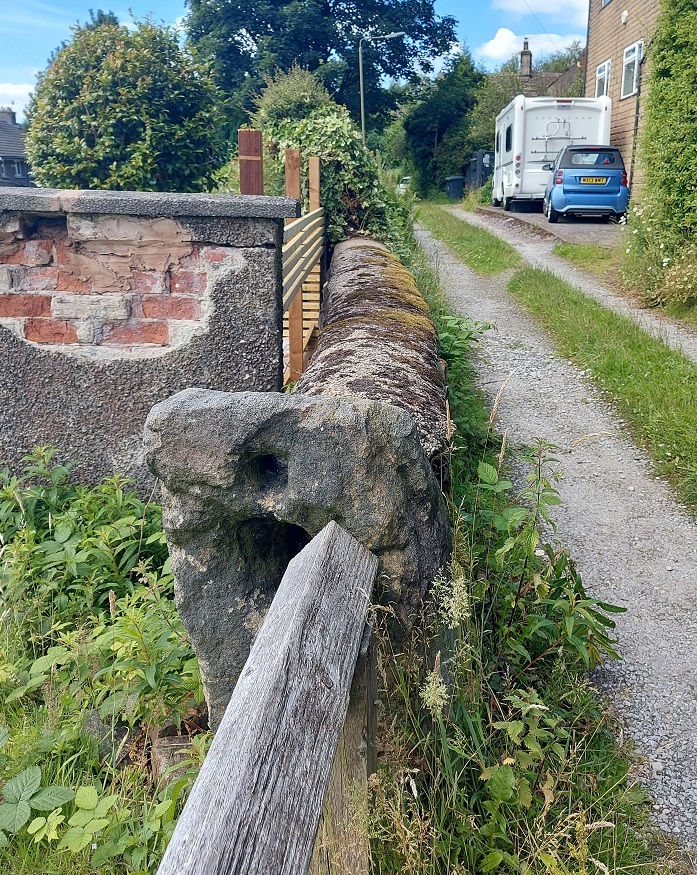

It was at that point it suddenly struck me, and as I stood there gasping like a stunned fish, ignoring the children, and mentally ran over all the holed stones I knew about (5 at that point). Of course, I thought, they all marked a junction in a footpath or track! And all of those tracks, I was fairly certain (and am now convinced) were the preservation of early (medieval or post-medieval) trackways between farmsteads. I have talked about this before – the fossilisation of early trackways, preserved as footpaths within modern settings, but in essence once the newer – and much better – roads were constructed for the mills (1790’s onwards), these old roads fell out of use, but as they often were more direct, and were known by locals who still used them, they gradually became public rights of way.
The stones, being big and heavy, are often not moved, so there they sit as testament to the tracks that were once the main roads between the dispersed settlements that made up Glossop. I know of 9 holed stones now (and two more that might be relevant), and looking closely at the stones, they all share similar aspects. Upright, and roughly shaped from millstone grit or similar gritstone, and they seem quite worn – usually an indicator of age. The hole, made through the stone, is broadly square in shape, measuring between 3 and 4 inches across, roughly carved, and placed in the top third of the stone. I am convinced they were shaped and set up by the same group of people to make using the notoriously bad road system around Glossop easier. Of the stones, the obvious question is why does it have a hole in it? My first thought was that it would mark the stone as different from others that might be in the area, making sure that a junction wouldn’t be missed in the dark or bad weather. This might be the case, but then I remembered reading that in 1693 a law was passed that trackways had to have a guide post showing destinations (the Whitfield Guide Stoop was a result of this law, but probably a later incarnation), and I wonder if the hole was there to allow a wooden sign to be placed in it with destination painted or carved on it? Or perhaps a simple stick pointing the way? Any thoughts on this, o’ wonderful readers? I also wonder how far this tradition continues – certainly I know of no others in surrounding areas – even Tintwistle or Hadfield, for example, seem to have no holed stones, although I’m happy to be proven wrong. .
But let’s have a virtual explore the Pyegrove to Glossop track here, starting at the stone that started it all.

Ignoring the A57/Snake Pass (opened in 1821, although bits are older), behind us is what is now Derbyshire Level, with the farmsteads of The Hurst, Jumble, and Gnat Hole, and also the road to Whitfield and Chapel en le Frith. Going left, then, a track along the edge of some houses leads out into Pyegrove Playing Fields.
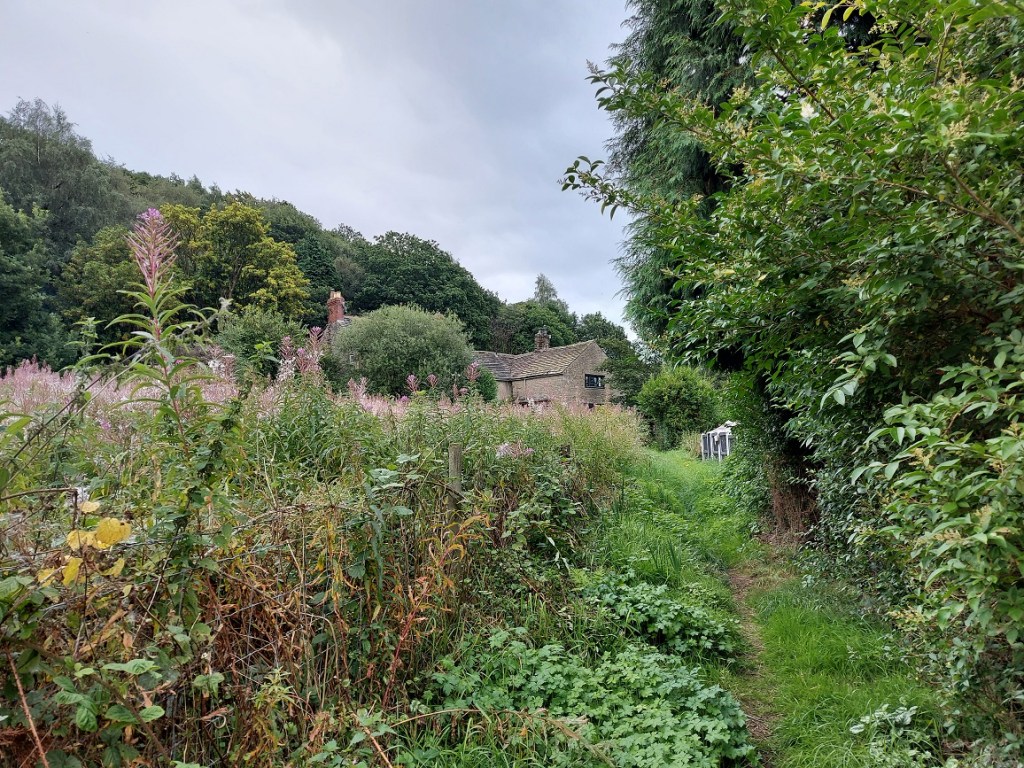

Along the northern edge of the playing fields the track is no longer used, but is visible as a ‘holloway’ – a track worn deep with use.

We join the track again at the corner of the playing field, where there is a lovely squared off standing stone.

This seems to mark the junction of a track that originates at Cross Cliffe, here marked in blue:

Whilst it is just about marked on older maps, it is no longer in use, although its memory is fossilised in this bit of unnecessary and unusually wide stretch of pedestrianised path leading from the Snake Pass to Pyegrove Park (marked with a red circle in the above map)
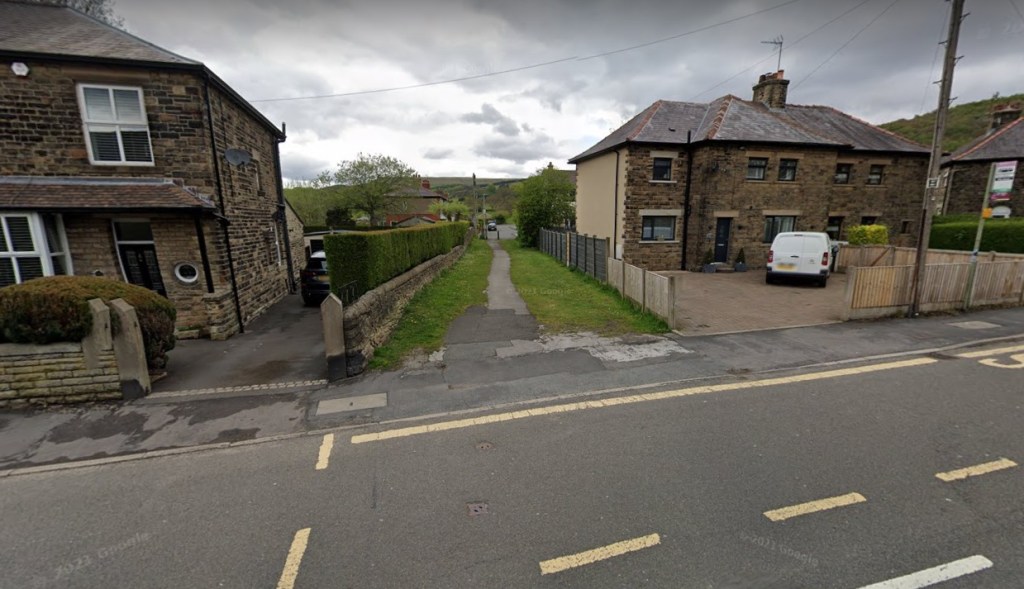

These simple – unholed – standing stones sometimes mark junctions, but more normally simply mark the line of a path where is might not be obvious, particularly in the dark or rough environment (I know of about 12 of these, too).
We continue along our Pyegrove track beyond the stone and past the remains of the Royal Observer Corps station. Briefly, the station was meant to monitor potential enemy aircraft in the immediate post-WWII period, but it would also serve as a monitoring post, observing and recording the effects of any nuclear detonation on Manchester – wind speed, radiation levels, blast radius, etc. This is why it is built into the hillside, 15ft below ground level. A sobering thought, and one sadly now relevant once more. This will also be the subject of a future blog post, don’t worry!
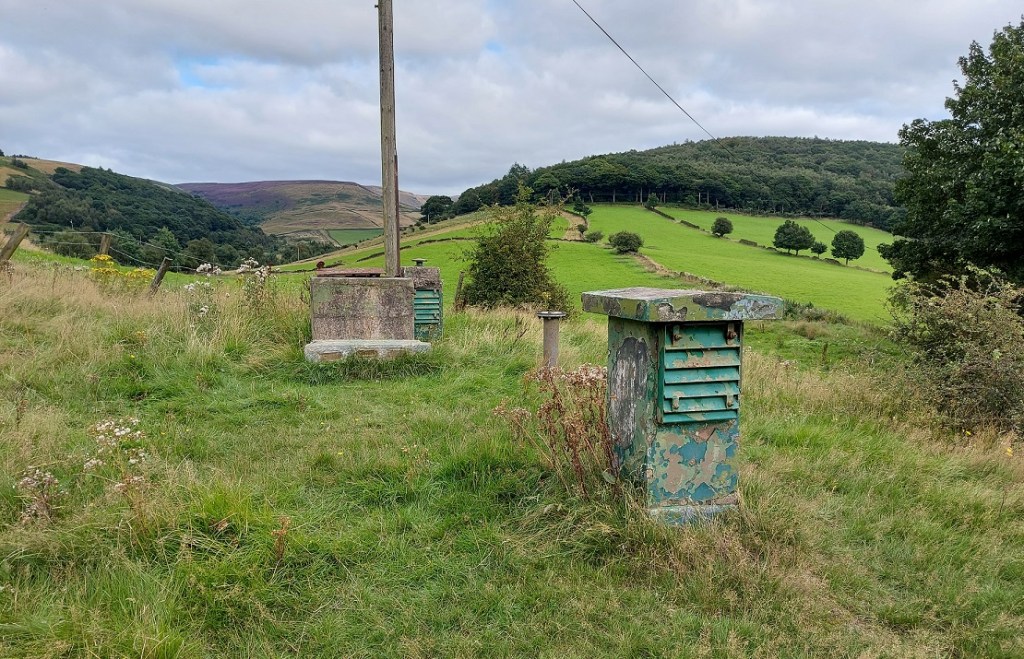

Back to the task in hand, and on to another standing stone. This one, looking for all the world like a gravestone, was originally one of a pair (its partner is embedded, horizontally now, in the wall.

These gravestone pairs are usually found mid track or at the start of junctions, and seem to be a later addition to the tracks (probably post-1790’s) and seem to be an attempt to force packhorses and traffic onto the newer roads (and presumably so they can pay the tolls) – and early form of traffic calming, if you will. I am fairly certain with the date of c.1800 as Whitfield Cross was used as a partner to one of these ‘gravestone’ pairings after it was moved in about 1800. There is some graffiti carved on the top of this stone – ‘G.B.’.
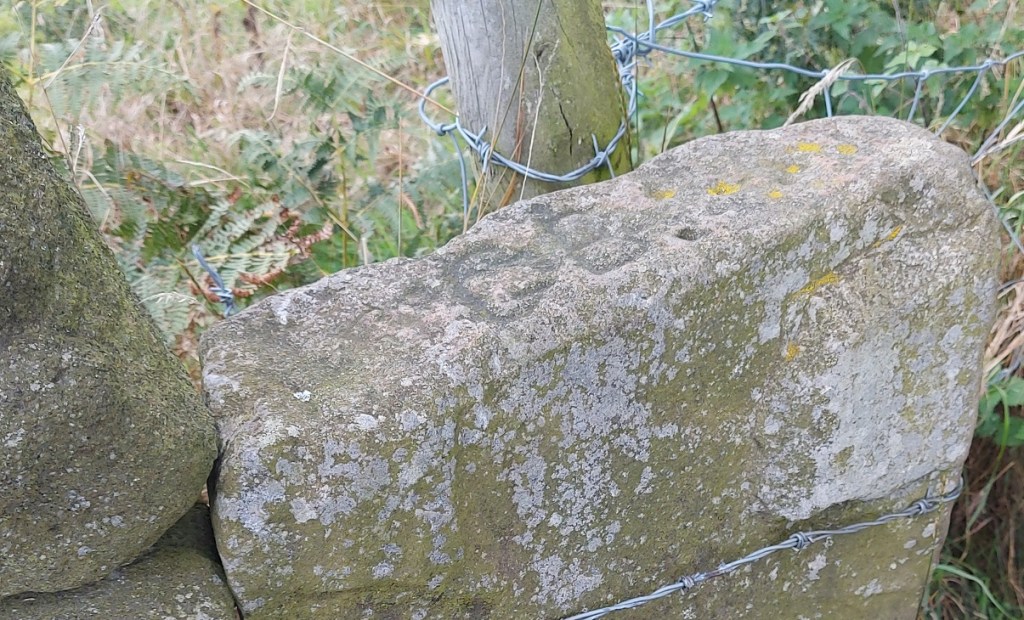

From here we continue, round the corner, to the farmstead of Hall Fold.

A datestone here records ‘J.S.J. 1806’, but this was apparently found when the owner was digging a foundation, and clearly Hall Fold Farm is older that that.

The name itself may refer to a long demolished, possibly medieval, original Glossop Hall (Manor Park Road was once known as Hall Street). This is also the location of a junction – our track is joined from one that comes from Whitfield (an extension of this one).
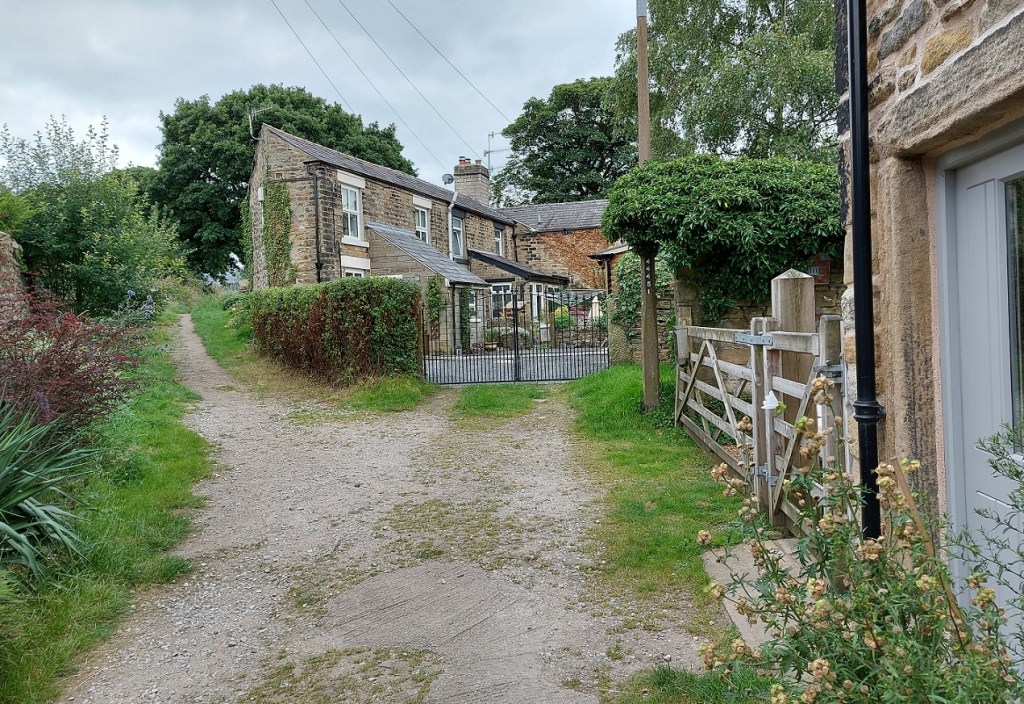

Our track from Pyegrove is on the left hand, but the one from Whitfield comes via Old Glossop Cricket Club, and would have come through the gates ahead. Though no longer in use, its presence is preserved in field boundaries and the fact that these houses (c.1830’s) respect the track, which is why they are built at that strange angle. It’s also visible in LIDAR under the cricket pitch.
Sadly, no marker stone remains at Hall Fold Farm (although I didn’t start poking around people’s gardens, and it may well be lurking somewhere – large stones are hard to completely lose). From here, the medieval centre of Glossop is a hop, skip and a jump… if you are feeling so inclined.
I have to say, though, walking into Glossop this way is a much more interesting – and authentic – experience, and one that is very different from walking along Manor Park Road! We take our modern roads for granted, and I’m not going to lie – the idea of moving along these tracks in bad weather and in darkness fills me with fear.
This is a small part of a much larger project I’m working on, tracing these tracks all over Glossopdale. Each of the settlements that make up ‘Glossop’ – from Wooley Bridge in the west, to Pyegrove in the east, Tintwistle at the north, to Chunal in the south – have multiple tracks linking them, and for the large part they are still there, often hidden, occasionally ‘fossilised’ as footpaths, or even still in use. This is truly an overlooked, and indeed largely undiscovered, aspect of Glossop’s pre-Victorian/pre-Industrial history, but one that was vital to its development. And I have to say it is great fun being able to walk these ways, and pondering the history they hold – if anyone fancies joining me, give me a shout. Also, and this is a serious request, if anyone knows of any holed stones (or any standing stones, for that matter) that I might not know about, please do get in touch – often half hidden in hedgerows, they will lurk where two or more tracks join.
Right, that’s all for now. More pottery next time (did anyone else hear that high-pitched screaming sound?), but until then look after yourselves and each other, and I remain,
Your humble servant,
RH.
Most interesting piece, thanks.
In the early to mid ’60s there used to be (what I would now call) a holloway which lead from the old Green Lane (when it was still a footpath or bridle way) to near Brookfield Methodist Church, passing a small children’s park (my key interest then). I think this r.o.w. still exists but doesn’t look like it takes the exact route as the one I would charge down anticipating the swings and roundabouts.
Looking at an old map I have this r.o.w. looks almost as if it was a virtual straight line from Hadfield Hall down Hadfield Road, into the older part of Green Lane, then continuing onto the ‘holloway’ down the hill into the open fields by the play area and onto the A57.
Hope this is of interest to you.
Regards
Colin
LikeLike
Our area has 12 “Domesday villages” – Simmondley, Arnfield and Crowden aren’t actually mentioned in Domesday, but they have Anglo-Saxon names so must have been there. 7 were definitely surrounded by open-field system, Dinting and Chisworth almost certainly weren’t. With limited exceptions – Lees Hall, Ashes, Old House, and possibly Hargate Hill, Little Padfield and Mossylea – there’s no clear evidence that any of them had “satellite” settlements in the mediaeval period, so the (very small) populations would have lived in the village centres and farmed the open fields and the common pasture beyond. Glossop’s open fields appear to have been enclosed in the 1580s, and that plus enclosure of the common would have led to the establishment of dispersed farmsteads – Heath, Blackshaw, Pyegrove. Even so, there were still 3 farms in the village itself in the early C20th.
There was a similar process in some of the other villages, but Chunal, for instance, is still largely frozen in its mediaeval form, and in Hadfield there were only ever two satellite farms – Lower and Higher Barn – there being still 4 farms in the centre in the late C19th. Dispersal continued into the C18th, the last major enclosures being Plainsteads (around 1790) and Whitfield Common after 1813. The local tracks (as distinct from the regional ways which ran through the area) would therefore have developed in phases, starting with links between the original AS villages (and after the church was built at Glossop in the 1100s, and the monks established markets at Glossop and Charlesworth, those on the Derbyshire side would have been linked to them). In addition to links between settlements, there would also have been droving tracks to gain access to common (Hadfield, for instance, had no access to any without going through neighbouring townships) and tracks into the hills to get peat and coal.
Very little of this complex network was carried over into the modern road system, which on the Derbyshire side was largely superimposed on it in the late C18th/early C19th by the Howard estate, the turnpike trusts (effectively controlled by the estate), and in Whitfield, which was mostly outside the estate, by the Enclosure Commissioners. The trusts then ruthlessly closed down “rat runs” around tollgates, such as Old Lane/How Lane in Simmondley which was the old way between Charlesworth and Glossop. However, they were daft enough to build along the valley bottoms, which the earlier travellers studiously avoided, with consequences we suffer every time there’s a cloudburst….
LikeLike